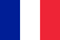
According to BME, prostatitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the prostate gland in men with damage to the parenchyma and interstitium. The treatment of prostatitis in men is a long and difficult event, most often due to complete ignorance of the disease in the beginning. What is prostatitis, what are the causes and the first signs, what you need to know about the subject of "diagnosis" and what modern methods of treating prostatitis exist. All men should know about prostatitis in this review article.
Ab ovo - from the egg
We are not talking about Horace's satires, in this case we are interested in everything related to prostatitis, from the very beginning to the last "squeak" of the treatment. Symptoms of prostatitis are found in men during active sexual activity, from 25 to 45 years, in a thematic video you can explore in detail everything related to the basics of the disease, its causes and symptoms, the peculiarities of diagnosis and treatment.
The reasons for the development of prostatitis are extensive. In prostatitis, infectious factors are most important in the development of the disease:
- Acute form. Coccal flora acts as provocative causes.
- Chronic form. The reasons for its development are more extensive, as the main factors of such prostatitis in men are: gonococci, Trichomonas, Gr + and Gr-bacteria, Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In rare cases, the diagnosis reveals mycoplasmas, viruses, fungi, chlamydia and others.
It should be noted that chronic prostatitis caused by a pathogen that has penetrated the prostate gland may later have a pathogenic factor and be abacterial in nature. The acute form is more often provoked by external causes: hypothermia, trauma to the urethra or damage to the bladder as a result of endoscopic examinations or various manipulations, hypodynamics and as a result of this violation of blood circulation and lymph in the pelvis (congestive prostatitis), hormonalor autoimmune disorders.
You can often hear about only one type of prostatitis - infectious, but according to the WHO, bacterial prostatitis accounts for no more than 10% of all cases, while chronic abacterial prostatitis is registered in 90% of cases.
Table No 1. Brief description of the pathology
> zxtable border = "1" cellpadding = "0" >The etiology of bacterial prostatitis in acute and chronic manifestations has been studied more fully, in most cases the bacteria of the family are the cause of the disease. Enterobacteriaceae (E. coli bacillus). The role of atypical microorganisms as a cause of prostatitis (ureplasma, chlamydia, mycoplasma) is currently considered not fully proven. Symptoms of prostatitis in men with signs of weakened immunity, especially in HIV, can be caused by yeast (Candida spp. ) Or Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Before the era of antibiotics, the gonococcal flora (Neisseria gonorrhoeae) played a significant role in the development of prostatitis, especially often causing its abscessive form.
The causes of the abacterial form of prostatitis have not been fully studied, although urologists have thoroughly studied the list of possible pathogenetic (provoking prostatitis) factors that play an important role in the occurrence of inflammation in the prostate without the presence of microorganisms. Thus, the causes of nonbacterial prostatitis are based on stagnant processes in the pelvis, circulatory disorders, intraprostatic reflux of urine and autoimmune aseptic inflammatory process.
Sick or not - that's the question
What does a man with prostatitis look like? For a person far from medicine and even more so who is not familiar with the problems of urology, the male appearance of one individual is no different from the crowd of others. And only an experienced specialist from the first complaints of the patient will understand where the root of the problem has matured and what ways to eliminate it will have to go.

The symptoms of prostatitis are often described in a few phrases, emphasizing the brightest moments and this plays a cruel joke with a man. Relying on such inaccurate definitions, he ignores really important bells, believing that the disease does not exist, although in fact the clinical picture depends on the nature of morphological changes in the prostate.
The earliest symptoms can be attributed to the following types of prostatitis:
- Catarrhal prostatitis. Dull pain in the perineum radiating to the sacrum, frequent urges at night.
- Follicular prostatitis. Difficult and frequent urination, sometimes late. Pain during "urination", intensifying at the end of the process of urination, as well as during defecation. Low-grade fever.
- Parenchymal prostatitis. There are symptoms of severe dysuria, often AUR, pain in natural recovery, general intoxication with a temperature up to 40 C.
In prostatitis with abscess formation, the symptoms are more pronounced with possible opening of the abscess in the rectum or in the prostate of the urethra. With such a breakthrough, the symptoms disappear. If an abscess opens in the paraprostate tissue or in the perineal area, visual symptoms may be observed: swelling, redness of the skin with pronounced fluctuations. At the same time, the man's condition is deteriorating sharply.
Comprehensive treatment of prostatitis can not begin without a thorough examination of the man, diagnosis and analysis of symptoms, which can directly indicate the type of disease.
In general, it is common to distinguish between acute and chronic prostatitis, on a thematic video on the Internet you can find out in detail which symptoms are related to one form or another. Let's look at this question in more detail.
Acute - its typical symptoms are characterized by the manifestation of three stages: catarrhal, follicular and parenchymal. They are described in detail above.
The most interesting in terms of symptoms is the chronic form of prostatitis, as there are many variations of symptoms. In general, the effective treatment of prostatitis depends on the prostatitis or rather on its type.
In the stage of chronization the following moments can be distinguished:
- Chronic prostatitis is rarely the result of an acute process.
- Primary prostatitis disappears with deleted symptoms.
- A characteristic symptom of chronicity is the scanty discharge from the urethra during defecation.
- The first symptoms, as a rule, are not expressed, the pathological process itself develops over the years. It is preceded by prostatosis (congestion in the capillaries), which gradually turns into an abacterial form of inflammation of the prostate gland.
- The specific pathogenic microflora is not the cause of chronic prostatitis, but the chronic process itself is a complication of the inflammatory process due to the effects of ureaplasma, Trichomonas, Chlamydia and Gonococcus.
How does a man with chronic prostatitis feel? Patient feedback shows that most often in the beginning there is a slight pain in the perineum, a scarce current, which most men simply do not pay attention. The next stage is the accession of the following symptoms: burning sensation in the urethra, sexual dysuria, malaise. Frequent improper ignition during sex makes men depressed, irritable or depressed.
It is important to understand that all these signs do not necessarily appear in each case of chronicity, this is what complicates the diagnosis at an early stage of the disease, in addition, the symptoms tend to change places, which is even more misleading.
Long-term syndromes
What can you expect from chronic prostatitis? If there is no timely diagnosis and treatment - nothing good, any specialist will confirm this. This type of prostatitis is characterized by 3 syndromes:
Pain
The prostate itself does not hurt, but many nerve endings pass through it and are nearby, which inevitably become involved in the inflammatory process. The pain can be of varying intensity - from mild pain, creating discomfort, to severe, not allowing you to sleep peacefully. Radiation pain occurs in all nearby areas (scrotum, sacrum, perineum), prostatitis pain should be differentiated from similar symptoms of other diseases.

dysuria
Dysuric syndrome always shows a malfunction in the urinary system, but the reason for this is revealed at the time of diagnosis. The increased volume of the prostate inevitably compresses the urethra and the flow of urine is disrupted, followed by the development of frequent urges to use the toilet, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. In advanced prostatitis there is compensatory hypertrophy of the muscular layer of the bladder and ureters. At this time, the symptoms of dysuria subside, but return to an intensified form.
Sex without pleasure
Declining intimate life - these are the first symptoms that men notice and it is they, as examinations show, force them to see a doctor. Frequent nocturnal erections, deleted orgasm, poor erection and rapid ejaculation, pain during it - this worries the strongest sex. At an advanced stage of chronicity, nothing good can be expected from prostatitis, erectile dysfunction often develops.
The degree of sexual dysfunction in men is not the same, someone begins sexual intercourse and somehow ends it, rejecting the characteristic bells. For some, even the initial weak response of the penis to a charming stimulus turns into a collapse and the beginning of sinister experiences that turn into prolonged depression. The specter of impotence is difficult for patients with prostate problems, almost always specialists and relatives notice that prostatitis spoils the character.
To learn more about the disease, you can study a thematic video where experts explain many of the nuances of pathology.
What to write on the map
What record will appear in the patient's medical record and what final diagnosis will be established depends on a series of primary examinations, starting from the patient's arrival at the urologist and his complaints (anamnesis) to the last stage of diagnostic measures. What exactly is required depends on the type of prostatitis, its neglect and the patient's consent to specific diagnostic procedures.
In general, the diagnosis consists of:
- Medical history. The doctor will ask in detail about all the complaints and symptoms, the preconditions of the disease, etc.
- Urine test.
- Prostate massage (digital rectal examination + collection of secretions).
- Prostate ultrasound.
- Spermograms.
- Prostate biopsy (if indicated).
What does diagnosis give and is it so important? If you read patient reviews, you can often see that most men try to avoid many stages of diagnosis, while the motives are very different. The price of such indifference is your own health! It is important to remember that prostatitis is treatable only if it is "caught" in time and the diagnosis is made precisely by defining the form of the disease and its cause.
How to become healthy forever
So, the man understands that he has prostatitis, what awaits him in the future and is it possible to regain lost health? It is important to understand that you will need to get rid of prostatitis 2 times longer than it has developed. In addition, if the pathological process is almost out of the man's attention, then the treatment of prostatitis will be carried out with his direct participation. Whether acute or chronic prostatitis can be cured - yes, if all the doctor's recommendations are followed, in advanced cases of chronic form, during treatment, it is possible to achieve a stable remission.

The stages of treatment for prostatitis will depend directly on what the doctor ultimately found during the examination, the type of disease, the patient's age and physical data.
The treatment regimen is always strictly individual, but the following points may be present:
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Physiotherapeutic methods.
- Phytotherapy.
- Appointment of immunocorrectors.
- Urological massage.
- Physiotherapy.
The cost of each stage of treatment is different, depending on the total cost of prescribed drugs, additional methods and the clinic. Preventive measures that follow the treatment have an important justification - they prevent the return of the disease. Prevention has direct and close contact with treatment, the basics of prevention are just as important as compliance with all the requirements of the doctor during therapy.
Treatment of the acute form
The period of exacerbation requires taking antibiotics, which are taken on a course. In the presence of chlamydial infection, drugs from the cephalosporin series are indicated.
The duration of the course is considerable, on average antibiotics are taken for at least 3-4 weeks to prevent recurrence of the disease. Sometimes the doctor continues the treatment for a longer period, antibiotics are combined with analgesics to relieve pain.
Treatment with antibiotics is carried out taking into account the following rules:
- Bacterial culture is required to determine the susceptibility of microorganisms to the drug.
- The side effects and contraindications of the drugs are taken into account.
- They take into account the previous course of treatment, when it was, what means were used and the result.
The need for additional methods of treatment is determined by the attending physician, it should be remembered that massage is contraindicated in acute prostatitis, as it provokes the spread of bacterial infection in the body, followed by bacteremia and sepsis.

Treatment of chronic form
It is important to remember that it is impossible to get rid of chronicity quickly, in general the disease has developed over the years and is beyond the power of even doctors in their field to destroy it in a few weeks, you do not need to take the word of thesewho cured the disease in 2-3 days. Treatment is aimed at stopping the source of the infection, restoring immunity in men and the work of the prostate gland, as well as preventing exacerbations - it takes time.
The course of antibiotic therapy lasts from 4 to 12 weeks, with low effectiveness of treatment, the drug continues to be taken. Most often, antibacterial drugs are prescribed in combination with other anti-inflammatory drugs. In advanced cases, surgery is performed with partial or complete excision of the prostate gland.
No bacteria or symptoms
A characteristic difference in therapy is the lack of antibiotics, without the presence of pathogenic microflora, they are simply not needed. But sometimes experts prescribe a short course of medication for 2-4 weeks.
The treatment of abacterial prostatitis is based on the use of physiotherapeutic methods: iontophoresis, ultrasound, laser therapy, electromagnetic radiation and symptomatic therapy to strengthen the patient's immune system.
Changes in diet and lifestyle are also at the heart of the treatment of nonbacterial prostatitis, baths, alpha-blockers are shown.
Asymptomatic prostatitis is difficult to detect, the diagnosis uses the PSA method, followed by the appointment of a 2-week course of antibiotics as treatment. Individual symptomatic treatment is then selected.
In general, the treatment of any type of prostatitis is a long-term phenomenon and is not always pleasant for the patient. Apart from the physical inconveniences, the man also suffers psychologically because his most valuable part of the body - the intimate one - is affected. Examinations of those who have cured the disease show that only strict adherence to the doctor's prescriptions, combined with diet and lifestyle changes, pays off. The cost of a frivolous attitude to treatment is very high - a person not only loses health, his whole life, character and relationships with others change. To prevent this, it is necessary to monitor the health of the prostate gland and eliminate the causes of disease.